

In general, lightly colored text should have a darker background and darkly colored text should have a light background. It is essential that appropriate contrast exist between text and the background. To assign this new heading style, select the text you wish to assign the style to, then click the paragraph style from the Paragraph Style menu. Select the Basic Character Formats located in the left side pane to customize the appearance of this new heading. Select Paragraph Styles in the Type drop-down menu.Ĭlick the drop-down menu button, than select New Paragraph Style. Items of equal importance should be equal level headings, and heading levels should not be skipped (i.e., a Heading 3 can't be the first heading after Heading 1 Heading 2 can't be skipped). Follow it with sub-headings (Heading 1) and sub sub-headings (Heading 2), etc. Start the page with a heading that describes overall document content (Title). Headings should be selected based on their hierarchy in the document. Such technologies ignore text size and emphasis (bold, italic, underline) unless Headings are used. Headings provide context and a way to navigate quickly for users of assistive technologies such as screen readers. This will automatically set a reading structure for your document.Ĭlick and drag elements to structure the reading order of the document. Then control-click the New Article icon from the Articles window.
Indesign tutorials windows#
Open up the Articles window by opening up the Windows drop-down menu, then clicking Articles. Documents with images, columns, text boxes, tables, etc., will require each of these to be manually checked or set to ensure assistive technologies progress through content correctly. To ensure that InDesign content is read in the correct order, reading order must be manually set. Type an alternative description in the box below, then click Done. Then select Custom from the Alt Text Source drop-down menu. In the Objects Export Options dialog box, select the Alt Text tab.
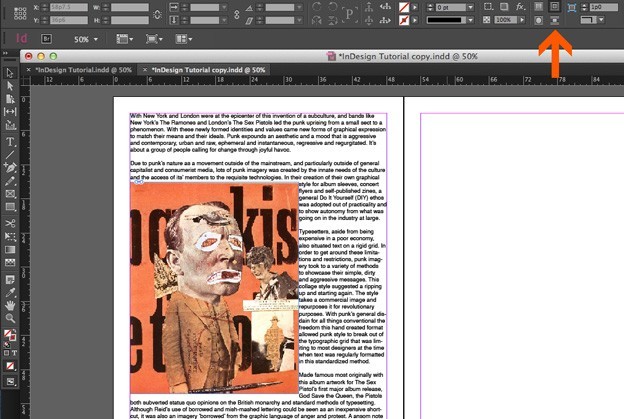
Select the image or object, then click the Object drop-down menu and click Object Export Options.
The more important an image's content is, the more descriptive the alternative text should be. While there are no hard and fast rules for determining what alternative text should say (it depends on the image, its context, the intent of the author, etc.), one simple trick is to imagine describing the image to someone over the phone. If the body of the document already contains a sufficiently detailed description in close proximity to the image, the alternative text can simply identify the image so that the reader knows when it is being referred to. Images used for purely decorative purposes (i.e., those that do not provide any meaningful information) should not have alternative text. Alternative text should provide sufficient information so that users who are unable to see them are still able to understand what they convey. This descriptive text should be limited to 120 characters for simple images, while the alternative text for graphs, tables, and complex images (such as detailed maps and diagrams) should give a brief summary of the included information. In this tutorial, the accessibility features of InDesign will be covered through:Īlternative text for images, charts, graphs, and tables is vital to ensuring that users with visual impairments have access to information included in these visuals. This tutorial was developed for InDesign CS6, although other versions may share functionality. This tutorial will walk users with InDesign through the use of these features. InDesign has a number of tools available to the user to make the content they create accessible. Creating Accessible InDesign Content Introduction


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
